Pharmacology and Safe Administration of Local Anesthetics
Learn about the pharmacology and safe administration of local anesthetics in dental sedation. Enhance patient care with effective and safe techniques.
Understanding Dental Sedation: A Comprehensive Guide for Dental Professionals
Dental sedation is an essential component of modern dental practices, offering patients a comfortable experience while enabling practitioners to perform procedures efficiently. Understanding the nuances of sedation, especially with local anesthetics, is crucial for dental professionals. Not only does it ensure patient safety, but it also enhances the effectiveness of the treatments.
In this post, we will explore key aspects of local anesthetics, their pharmacology, administration, and potential complications. These are all essential for optimizing patient outcomes in dental sedation. By refining sedation techniques, dental practitioners can minimize risks while maximizing comfort for their patients.
Mechanism of Action and Pharmacology of Local Anesthetics
At the core of dental sedation lies the effective use of local anesthetics. Local anesthetics work as sodium channel blockers, preventing sodium ions from traversing nerve membranes. This blockage inhibits the propagation of nerve signals, effectively numbing the area to pain. The three key factors that influence how different local anesthetics function are:
- Dissociation constant (pKa): The pKa of an anesthetic determines how much of the drug becomes ionized and how easily it crosses cell membranes. Anesthetic drugs work optimally in tissues with a neutral pH, but in infected or inflamed areas where the pH drops, their effectiveness can be compromised.
- Protein binding: Drugs that bind to proteins in the tissues exhibit longer durations of action. Bupivacaine, for example, has high protein binding, which prolongs its anesthetic effect. On the other hand, drugs with lower protein-binding capacities, like Articaine, may have a shorter duration but faster onset.
- Lipid solubility: The more lipophilic (fat-soluble) an anesthetic, the more potent it is. Bupivacaine, due to its higher lipid solubility, requires a lower concentration to achieve effective anesthesia compared to Articaine, which has a lower lipid solubility but is used at higher concentrations.
Choosing the Right Local Anesthetic
Choosing the appropriate anesthetic for a procedure depends on factors like duration of action, onset time, and potential risks of toxicity. Below are a few examples:
- Articaine (pKa 7.8): Common in dental practice, it offers a rapid onset of action with a relatively short duration. Articaine is favored for its ease of use, but practitioners should be cautious when using it in younger patients (especially under 4 years of age) due to increased risk of complications.
- Bupivacaine (pKa 8.1): Known for its prolonged duration of action, Bupivacaine is an ideal choice for longer procedures. However, its slower onset makes it less suitable for quick, short procedures.
- Procaine: As a prototypical anesthetic, Procaine has fallen out of favor due to its short half-life and weak potency. It is not recommended unless epinephrine is added to counteract its vasodilatory effects.
Managing Anesthetic Dosage and Toxicity
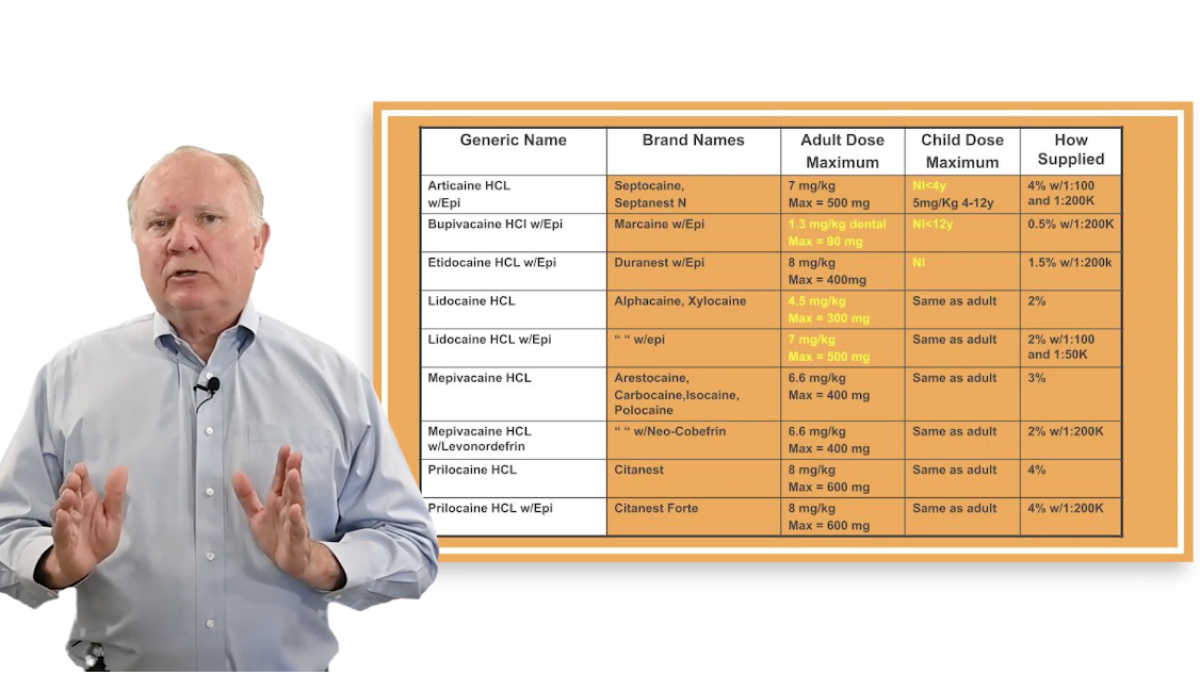
Local anesthetic toxicity is a major concern when administering sedation. Understanding dosage limits is vital to avoid complications. Lidocaine, for example, has a maximum recommended dose of 500 mg for a healthy adult. However, dental professionals should always be cautious and mindful of individual patient sensitivity.
In patients with cardiovascular issues, the maximum dose of epinephrine must be carefully considered. For example, while a healthy adult can tolerate up to 0.2 mg of epinephrine per visit, patients with cardiovascular disease should not exceed 0.04 mg. Over-administration of epinephrine can lead to complications like tachycardia, hypertension, or, in severe cases, heart block.
Adverse Effects and Contraindications
Like any medication, local anesthetics come with potential side effects. Among the most common are:
- Allergic reactions: Typically associated with ester-based anesthetics like Procaine.
- Cardiovascular depression: Bupivacaine and Etidocaine, due to their strong protein-binding characteristics, can cause significant cardiovascular depression, potentially leading to severe complications like heart block. Patients with heart disease should be carefully monitored during sedation.
- Central nervous system effects: Overdose or intravascular injection of local anesthetics can lead to symptoms like anxiety, twitching, or more serious consequences such as seizures and coma. Practitioners must always aspirate before administering the drug to ensure the injection is not intravascular.
Preventing and Treating Anesthetic Overdose
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of complications during sedation. Staging injections over time, instead of delivering the full dose at once helps to limit peak blood levels of the anesthetic. Additionally, using small-gauge needles can minimize the risk of intravascular injection.
In the rare event of local anesthetic toxicity, treatment should focus on supportive care, ensuring the airway is maintained, and providing oxygen. For more severe cases, particularly when cardiovascular or central nervous system symptoms arise, interventions like intravenous administration of lipid emulsions (such as Intralipid) may help by absorbing the circulating anesthetic, reducing its neurotoxic effects.
Learn more with Dr. Joe Seay
The safe and effective administration of local anesthetics is critical in providing comfortable dental care while minimizing risks. As dental professionals, mastering the pharmacology, dosing, and proper techniques of sedation ensures patient safety and enhances the quality of care, particularly in pediatric settings where precise sedation is crucial.
To further enhance your expertise, we invite you to enroll in the Pediatric Endorsement Sedation Course. This course offers 16 CE credit hours and is tailored to equip you with the necessary skills to safely administer sedation and anesthesia to pediatric patients. You’ll learn from top industry experts like Dr. Joe Seay, DDS, MS, a Diplomate of the American Dental Board of Anesthesiology, who brings over 30 years of experience in the field. Dr. Seay has extensive training in pharmacology, having studied pharmacy and dentistry at the University of Oklahoma and completing his anesthesia residency at The Ohio State University.
You’ll gain in-depth knowledge about pre-anesthetic assessments, emergency procedures, sedation pharmacology, and much more, ensuring you're prepared to meet the Texas State Board of Dental Examiners (TSBDE) requirements and elevate your practice.
Don’t miss this opportunity to enhance your sedation skills, ensure patient safety, and stay ahead in pediatric dental care. Enroll today in the Pediatric Endorsement Sedation Course and continue your professional growth.
 Sani Leauanae
Sani Leauanae 